Methodology
SUSTAIN-6G – in the role of a Lighthouse Project – will be the driving force within the SNS JU for activities that have been – and are conducted – towards improving sustainability holistically in 6G systems, by addressing the six defined project objectives.
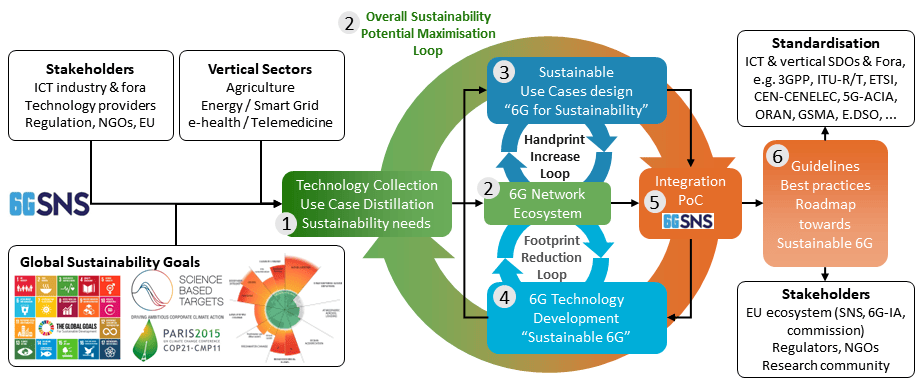

SUSTAIN-6G will link sustainability goals and solutions towards a state-of-the-art technology collection, a set of important use cases, and the needs of stakeholders and vertical sectors (Objective 1):
- Global sustainability goals (e.g., UN Sustainable Development Goals, Science Based Targets initiative)
- Research and innovation from previous and ongoing projects (including SNS projects, Coordination and Support Actions (CSAs), and relevant nationally funded projects)
- The relevant regulatory frameworks (e.g., AI Act, General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), European Green Deal, EU Taxonomy, Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation, Waste of Electrical and Electronic Equipment Directive, Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive)
- Sustainability requirements set out in the ICT sector, e.g., through GSMA or NGMN
- Specific vertical requirements and solutions in the three sectors selected by SUSTAIN-6G: Agriculture, e-Health / Telemedicine, and Energy / Smart Grid (*).
To enable a common sustainability framework in the context of 6G, SUSTAIN-6G will drive forward the standardised metrics, processes and methodologies (Objective 2) to define and assess, and thereby allow to maximise the sustainability potential in 6G systems:
- Generic, technology-specific, and use case-specific metrics (values as goal/outcome, key values, key value indicators, key performance indicators) to make sustainability in all three areas (environmental, societal, economic) qualitatively and quantitatively measurable in a standardised way
- Harmonised processes and methodologies (e.g., as a further evolution of the Key Value Indicator process) that enable a standardised definition of sustainability metrics and their evaluation
- ECO-design concepts for connected and circular devices


Towards sustainability improvements through reducing Footprint and improving Handprint, SUSTAIN-6G will develop and evolve ideas, create innovation, and develop concepts and solutions by addressing gaps in technology and methodologies in both sustainability aspects, 6G for Sustainability and Sustainable 6G.
- 6G for Sustainability (Objective 3) – enhance integration of vertical use cases (for the envisaged sectors) with 6G technical solutions as enablers for making vertical applications, services and systems more sustainable; further use cases will be linked based on the use case analysis conducted by Objective 1
- Agriculture: Connectivity on demand – temporary connectivity solutions in rural areas; Task offloading to the edge for critical and resource-demanding tasks; Agriculture data vs information (e.g. from sensor grids)
- Energy: 6G enabled smart grid balancing services; Resilient smart grid section operation; Joint planning of 6G and smart grid infrastructures
- E-Health: Concurrent connected preoperative surgical and engineering planning (implants / prostheses); Remote rehabilitation assessment for patients; Medical data federation (generic)
- Sustainability management plan and services for the seamless end-to-end integration of vertical with 6G ICT ecosystems
Sustainable 6G (Objective 4) – complement the portfolio of 6G technologies identified in the technology collection conducted by Objective 1 by further promising technologies in all network domains
- Radio Access Network (RAN): RAN energy consumption (components, modelling, evolution); energy-aware RAN operation, Optimised low density parity check
- Optical network: Wired and wireless optical solutions for a photonic continuity – All Optical Network (AON); Fixed-mobile convergence with Fronthaul / Crosshaul / Midhaul
- Network management under mixed constraints and joint communication & computation optimisation
- End-to-end solutions: Network end-to-end enablers for optimal energy efficiency; Cloud infrastructure for energy efficient cloud-native network functions; Energy efficient and sustainable AI-native 6G networks; Responsible AI


SUSTAIN-6G will be a hub to validate and evaluate sustainability (Objective 5) impact through Proof-of-Concept (PoC) with implications of verticals, in close collaboration with other SNS reasearch projects, including, e.g., projects working on specific sustainable technology solutions, and large trials.
Concepts, solutions, and insights as well as proven methodologies will be consolidated into guidelines, best practices, roadmaps, and standards contributions (Objective 6), to drive the full integration of sustainability into future communication and vertical systems, for use across the European Union (EU) and beyond.
- This consolidation will be conducted in close collaboration with stakeholders and other SNS projects to ensure that 6G solutions are sustainable and support sustainability in other industries, enabling socio-economic improvements for large enterprises, Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) and communities, and protect and enhance natural, human, and social capital.
- The outputs and impact of SUSTAIN-6G will enhance existing and encourage new ecosystems and business models to develop and thrive within planetary boundaries, and strive to protect and restore the environment.

(*) The 3 vertical sectors selected by SUSTAIN-6G, where UCs will be worked out in detail, put requirements on the full spectrum of ICT technology such as coverage, throughput, latency, reliability, or security, and they address a broad spectrum of goals and values in all three sustainability areas, e.g. Trustworthiness, security, privacy, impact to biodiversity, material use, energy efficiency, and digital inclusion. Thereby, results and insights from the analysis of these use cases can be extrapolated to other verticals sectors such as smart cities or education.

