Motivation

The current work in research and standards towards sustainability in 6G systems has a set of key shortcomings:
-
- The handprint and footprint in 6G systems cannot be targeted in isolation – there is a strong interrelation and trade-off between ICT and vertical systems. Handprint and footprint refer to the direct negative sustainability impact and the induced negative or positive sustainability impact, see Terminology.
- Most currently investigated and developed solutions target only specific domains or technologies (e.g., radio access, transport, artificial intelligence) – there is a scattered landscape of solutions.
- Most currently investigated and developed solutions incompletely cover sustainability areas and lifecycle phases – for example, only the operational phase of assets with a focus on energy efficiency.
- Sustainability related solutions are often not yet applicable to practical implementations, in particular with respect to processes and methodologies for defining and assessing sustainability metrics and gains.
To overcome these shortcomings, SUSTAIN-6G will lead the way towards a holistic perspective of sustainability in the context of 6G.
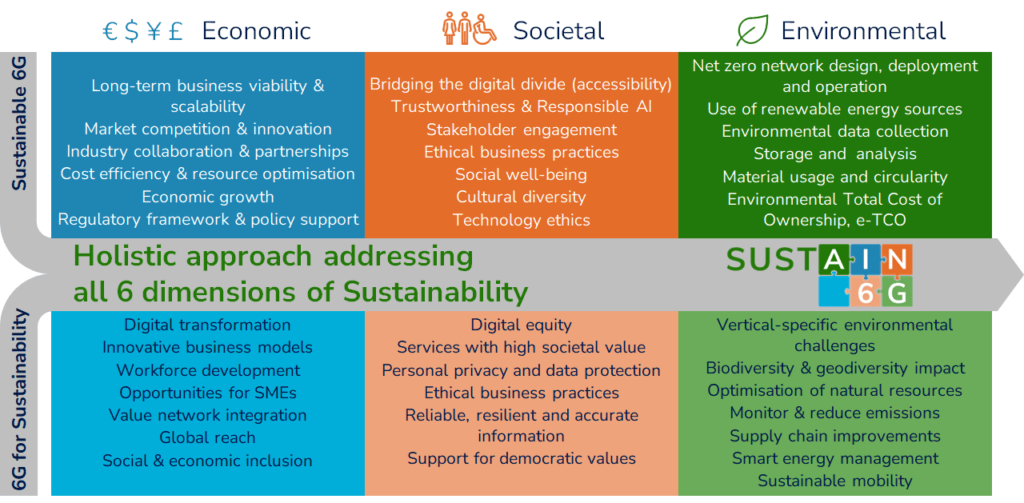
- Jointly addressing all six dimensions of sustainability in the context of 6G, namely the three areas of sustainability – environmental, societal, economic – for both aspects of sustainability, “Sustainable 6G” technology and “6G for Sustainability” in vertical scenarios (see figure below
- In an end-to-end manner, from device (e.g., a sensor, vehicle or handheld) to service (e.g., a harvesting forecast or an augmented reality rehabilitation application) across all network domain
- Considering the full lifecycle of assets, from network and service design via planning, implementation, deployment, operation to phase-out and disposal
- Bringing processes and methodologies to practice, to define standardised sustainability metrics, and enable to validate and evaluate sustainability gains and trade-offs.
-
-

